CNC machining is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. It stands for Computer Numerical Control, a technology that automates machine tools.
This process is vital for creating precise parts and components. It uses computer programming to control machinery, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
CNC machines can perform a variety of tasks. They can mill, turn, drill, and cut materials with high precision.
The technology is used across many industries. From aerospace to automotive, CNC machining is essential for producing complex parts.
CNC machinists are skilled professionals. They operate and maintain these machines, ensuring smooth production processes.
Learning about CNC can open doors to various career opportunities. Many institutions offer CNC classes and training programs.
Understanding CNC technology is crucial for anyone in manufacturing. It combines computer programming with mechanical operations to achieve remarkable results.
In this article, we will explore the meaning, applications, and benefits of CNC machining.
CNC Meaning: What Does CNC Stand For?
CNC is an abbreviation for Computer Numerical Control. It refers to the automation of machine tools through software and computers. This technology enables precise control over machinery operations using programming.
CNC technology emerged from early numerical control methods. Initially, machines were controlled with punched paper tape. Today, computers perform this task, providing enhanced capabilities and efficiencies in manufacturing processes.
The essence of CNC lies in its computerized control systems. These systems interpret coded instructions, directing machines to perform specific tasks with exactness. This process minimizes human intervention, reducing the margin for error.
The fundamental components of CNC include the following:
- Computer: Runs the software.
- Controller: Processes instructions.
- Machine tool: Executes operations.
CNC machines perform various tasks with high precision. This adaptability allows them to engage in numerous industries, producing complex parts that meet stringent specifications. Thus, CNC technology supports diverse manufacturing needs.
Industries benefit significantly from CNC technology. It delivers consistency and precision across a wide range of applications, from crafting intricate medical devices to constructing robust automotive parts. The technology has redefined modern production.
In summary, CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control, a key player in the manufacturing world. This system integrates computers with machines to deliver efficient, precise, and repeatable operations.
The History and Evolution of CNC Technology
CNC technology has a rich and fascinating history. It began in the 1940s and 1950s when engineers sought ways to improve manufacturing precision and efficiency. Early CNC systems were a mechanical challenge, relying on punch cards to input data.
The 1960s saw the introduction of more advanced systems. These featured rudimentary computers that streamlined data processing. The innovations paved the way for more efficient production capabilities across multiple industries.
As technology progressed, so did the software. By the 1970s and 1980s, CNC machines were using minicomputers that offered enhanced speed and flexibility. This evolution marked a significant leap in machining accuracy and complexity.
Key milestones in CNC development:
- 1940s-50s: Birth of basic numerical control.
- 1960s: Introduction of primitive computer systems.
- 1970s-80s: Advances in programming software.
Modern CNC machines integrate sophisticated computer technologies. These include high-speed processors and advanced software, which offer unparalleled precision and efficiency. The machinery is now part of smart manufacturing ecosystems worldwide.
Today, CNC technology continues to develop. It incorporates cutting-edge features, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), enhancing the industry to unforeseen levels. These innovations ensure CNC machining remains a key player in modern manufacturing.
How Does CNC Work? The Basics of Computer Numerical Control
At its core, CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control. This technology automates machine tools through computer programming. It transforms digital designs into precise physical parts.
The CNC process begins with a design created in Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This digital model serves as the blueprint for machining. Engineers then convert this design into instructions using Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software.
CNC machines read these instructions through a CNC program code called G-code. This code guides every movement of the machine tools, ensuring accuracy and repeatability. The machine follows the G-code commands to carve, cut, or shape the workpiece.
Key aspects of how CNC works:
- CAD Software: For designing parts.
- CAM Software: Converts designs into machine instructions.
- G-code: Directs machine movements.
- Machine Tools: Perform the physical operations.

A CNC controller executes the G-code commands. This sophisticated computer system manages the machine's operations. It ensures each movement aligns with the intended design.
With precise control over tools, CNC technology creates complex geometries with ease. Engineers can produce intricate designs that would be challenging with manual operations. CNC machining enhances productivity by minimizing human errors and increasing speed.
Lastly, CNC machines are versatile, used for various operations like milling, turning, and cutting. This adaptability makes them essential in different industries, from aerospace to medical manufacturing. The result is a manufacturing process that is efficient, reliable, and consistent.
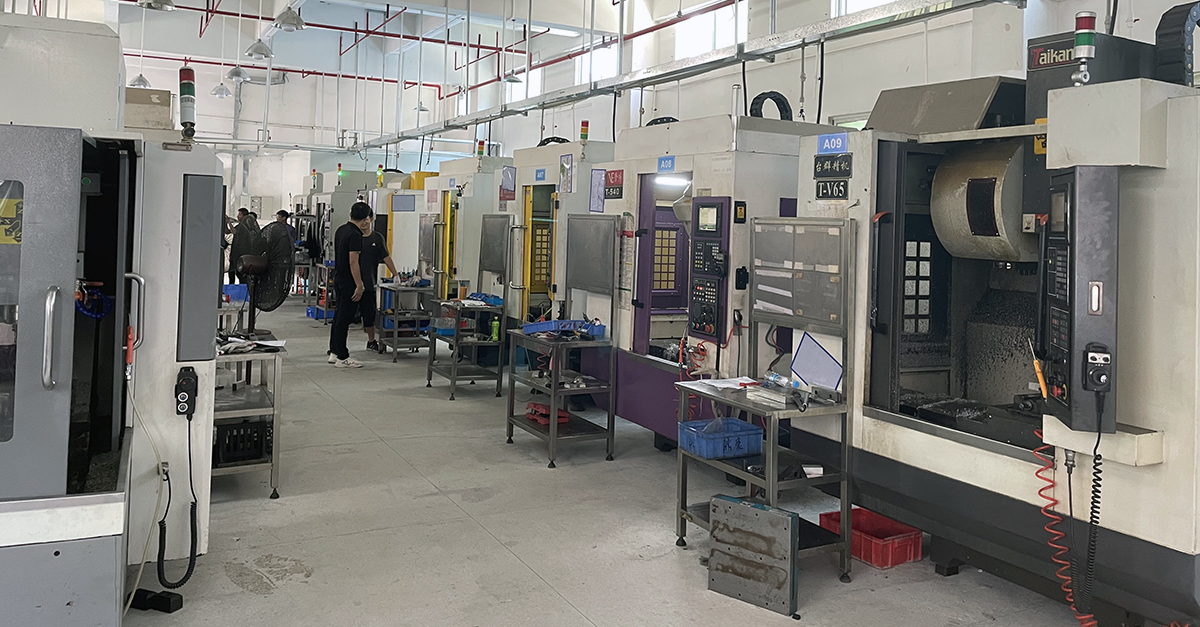
Key Components of a CNC Machine
CNC machines consist of several critical components that work harmoniously to create precise parts. Understanding these components is essential to grasp how CNC machines operate.
The controller serves as the brain of a CNC machine. It reads and interprets the G-code instructions, ensuring accurate execution of every command. This component manages tool movement, speed, and feed rate, maintaining precision and repeatability.
Next is the machine tool, which physically interacts with the workpiece. This component shapes, cuts, or drills the material based on instructions received from the controller. Common machine tools include mills, lathes, and routers.
Each CNC machine also includes a spindle, which is crucial for the machine's motion. The spindle holds and rotates the tool, driven by motors, to cut or shape the material. Its speed and power determine the machine's effectiveness.
Additionally, CNC machines feature a drive system. This system consists of motors and mechanical components that control the machine's motion along different axes. It ensures fluid and precise movements necessary for intricate operations.
Finally, the worktable securely holds the workpiece during machining. This stable platform prevents any unwanted shifts, ensuring consistency and accuracy throughout the process. The worktable's design varies, accommodating different sizes and types of materials.
Key components of a CNC machine:
- Controller: Interprets and executes G-code.
- Machine Tool: Performs cutting and shaping.
- Spindle: Drives tool motion.
- Drive System: Manages movement along axes.
- Worktable: Holds the workpiece securely.

By understanding these components, one can appreciate the complexity and precision that CNC machines bring to modern manufacturing.
Types of CNC Machines and Their Applications
CNC machines come in various types, each suited for specific tasks and industries. They streamline manufacturing processes with versatility and precision.
CNC milling machines, or mills, are widely used for cutting and shaping solid materials. They use rotary tools to remove material, crafting parts with complex shapes and high accuracy.
CNC lathes, on the other hand, are designed for material removal via rotation. They are excellent for creating symmetrical objects like cylinders, cones, and spheres.
Another popular machine is the CNC router. It's adept at cutting and engraving wood, plastic, and lightweight metals, making it a favorite in furniture and signage production.
Plasma cutters use high-velocity ionized gas to slice through metal. They're ideal for cutting thick sheets of steel or aluminum swiftly and accurately.
Laser cutters employ focused light beams to cut or engrave materials. Precision and clean edges are their hallmarks, common in intricate design jobs.
Waterjet cutters use high-pressure water streams mixed with abrasives to cut through tough materials. They prevent heat damage, suitable for sensitive applications.
Applications of CNC machines include:
- Aerospace: Precision parts for aircraft.
- Automotive: Engine components and body parts.
- Electronics: Circuit boards and enclosures.
- Furniture: Custom designs and intricate patterns.
These machines revolutionize various sectors by producing intricate parts quickly and reliably.

CNC Mills
CNC mills specialize in vertical or horizontal cutting, driven by computer software. They employ rotating cutters to remove material from a fixed workpiece. Mills are versatile, handling various materials like metal, plastic, and wood. They excel in creating detailed parts for automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries.

CNC Lathes
CNC lathes perform tasks by rotating the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool. They're perfect for crafting components with radial symmetry, such as shafts and pulleys. Widely used in the automotive and tooling industries, lathes ensure smooth finishes and high precision, even for intricate designs.

CNC Routers, Plasma, Laser, and Waterjet Cutters
CNC routers cut various materials with speed and precision, ideal for woodworking and crafting intricate designs. Plasma cutters rely on ionized gas for slicing metals, excelling in jobs requiring swift execution. Laser cutters utilize focused light beams for accurate cuts, perfect for delicate tasks.
Waterjet cutters offer versatility, cutting with a mix of water and abrasives. Their no-heat process suits temperature-sensitive jobs. Each of these machines brings unique advantages, broadening CNC applications in creative and industrial fields.
- Routers: Woodworking, signage.
- Plasma: Quick metal cutting.
- Laser: Detailed precision work.
- Waterjet: Heat-sensitive material applications.

CNC Programming: Languages, Software, and Workflow
CNC programming is the backbone of operating CNC machines efficiently. It involves creating a set of instructions that guide machine operations and movements.
Languages like G-code and M-code are central to CNC programming. G-code specifies machine movements, such as paths, feeds, and speeds. Meanwhile, M-code manages machine functions, like starting and stopping operations.
Software plays a crucial role in CNC programming. CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is used to create and modify designs. Once the design is ready, CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software converts it into CNC programs.
These software solutions streamline the workflow, from design to final product. They provide simulations to visualize machining operations, reducing errors and optimizing tool paths.
A typical CNC workflow involves several key steps:
- Design Creation: Generate a digital model using CAD software.
- Toolpath Generation: Use CAM software to define machining paths.
- Simulations: Run simulations to verify toolpaths and avoid collisions.
- Exporting Code: Convert paths into G-code or M-code.
- Machine Setup: Prepare the CNC machine with appropriate tools and materials.
- Execution: Upload the code to the CNC controller and start machining.
- Finishing: Perform inspections and adjustments for final touches.
The advantages of CNC programming include automation, precision, and efficiency. It allows production of complex shapes with minimal manual intervention.
Learning CNC programming offers career opportunities in varied industries, from manufacturing to aerospace. Training courses and online resources provide essential knowledge and skills to become proficient in this field.
Mastering CNC programming is crucial for anyone aspiring to work with CNC technology, offering the ability to transform digital designs into tangible objects with precision and speed.

The CNC Machining Process: From Design to Finished Part
The CNC machining process begins with a concept, transforming into a tangible product. It involves several essential stages, each critical to the final outcome.
Design Phase
First, a designer creates a 3D model of the part using CAD software. This software enables detailed visualizations and modifications before production begins.
Program Generation
Next, the CAD model imports into CAM software to generate CNC programs. This step translates design specifications into machine-readable instructions.
Toolpath Verification
Verifying toolpaths is crucial in ensuring efficient and collision-free machining. Simulations in CAM software highlight potential issues and optimize tool movements.
Setting Up the Machine
Once the program is verified, the CNC machine is set up. This involves loading the necessary tools and materials according to the program's requirements.
Execution of Machining
The machine executes the program, with precise movements dictated by G-code. The CNC machine carves out the part, layer by layer, following exact specifications.
Inspection and Quality Control
Quality checks ensure the part meets all design criteria. Measurements and inspections identify any deviations, allowing adjustments if necessary.
Finishing Processes
Finally, post-machining processes like polishing or coating enhance the part's aesthetics and performance. These finishing touches complete the manufacturing process.
Summary of the CNC Machining Process
- Design in CAD
- Generate CNC Program in CAM
- Verify Toolpaths
- Set Up the Machine
- Execute Machining
- Inspect and Adjust
- Finish the Part
Each stage of the CNC machining process is vital to producing high-quality parts. This workflow exemplifies the precision and efficiency CNC technology brings to modern manufacturing.

Materials Used in CNC Machining
CNC machining is versatile, suitable for various materials. It can handle metals, plastics, and composites with remarkable precision.
Metals in CNC
Metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium are commonly used in CNC machining. Each metal offers unique properties such as strength, weight, and corrosion resistance.
Plastics and Composites
Engineering plastics such as ABS, acrylic, and polycarbonate provide lightweight options. Composites like carbon fiber offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios, useful in specialized applications.
Material Selection Considerations
When selecting materials, factors like machinability, cost, and end-use requirements are crucial. The chosen material impacts the final product’s performance and durability.
Commonly Machined Materials
- Aluminum
- Steel
- Titanium
- ABS Plastic
- Acrylic
- Polycarbonate
- Carbon Fiber
Each material possesses characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. CNC machines can adapt tools and techniques to optimize machining for these diverse materials.

CNC technology's adaptability to various materials underscores its importance in manufacturing. It allows the creation of precise and high-quality components across multiple industries.
CNC Machinist: Roles, Skills, and Training
CNC machinists play a vital role in the manufacturing industry. They operate and maintain CNC machines to produce precision parts.
Key Responsibilities
A CNC machinist must set up machines, ensuring the correct tools and materials are in place. They also monitor the machining process to maintain quality.
Essential Skills for CNC Machinists
Proficiency in interpreting technical blueprints is crucial. CNC machinists need solid mathematical skills for calculating dimensions and tolerances.
Training and Certification
While some machinists gain skills on the job, formal training is often beneficial. Many pursue education through vocational schools or community colleges.
Opportunities for Certification
Certifications from recognized institutions, like the National Institute for Metalworking Skills (NIMS), enhance job prospects and credibility in the field.
Career Progression
Experienced machinists may advance to supervisory roles or specialize in areas like CNC programming. Continuous learning is essential in this ever-evolving field.
Key Skills for CNC Machinists
- Technical blueprint reading
- Advanced mathematical ability
- Proficiency in using CNC software
- Strong problem-solving skills

Pursuing a career as a CNC machinist offers rewarding opportunities. It combines technical expertise with practical applications, critical to modern manufacturing. With advancements in CNC technology, the demand for skilled machinists continues to grow.
CNC Services: What They Offer and How to Choose
CNC services provide specialized machining solutions across various industries. They cater to both small and large-scale production needs.
Offerings of CNC Services
These services include custom machining, prototyping, and production runs. They also offer CNC milling, turning, and complex machining operations.
CNC service providers often work with a variety of materials. Metals, plastics, and composites are common materials in their projects.
Choosing the Right CNC Service
Selecting the right CNC service involves several considerations. First, evaluate the provider’s expertise in handling your specific project requirements.
Factors to Consider
- Material Compatibility: Ensure they can machine the materials you need.
- Equipment Capability: Check if they have advanced, modern machinery.
- Experience and Reputation: Look for providers with a proven track record.

Final Thoughts
The right CNC service provider can significantly impact your project's success. Thorough research and comparison can help you make an informed decision. Opt for a provider that aligns with your technical and budgetary needs. Experience and precision should be priorities when choosing among CNC services.
Advantages of CNC Machining
CNC machining has transformed modern manufacturing with its multitude of benefits. This technology offers precision, efficiency, and versatility that traditional methods can't match.
Enhanced Precision and Consistency
One of the major advantages is its ability to produce parts with exceptional precision. CNC machines achieve consistent results, minimizing human errors and variations between production runs.
Efficiency and Speed
Another benefit is the significant reduction in production time. CNC machines operate rapidly and can run continuously without breaks, boosting productivity.
Versatility and Flexibility
CNC machining is also highly versatile, accommodating various materials and complex geometries. It can swiftly switch between different projects or materials with minimal downtime.
Key Benefits of CNC Machining
- High Precision: Ensures tight tolerances and accurate dimensions.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces waste and labor costs.
- Scalability: Suitable for both small and large production runs.
- Material Range: Works with metals, plastics, and composites.

In summary, CNC machining is ideal for industries demanding high quality and repeatability. Its advantages make it a staple in modern manufacturing processes, driving innovation and efficiency.
Limitations and Challenges of CNC Machining
Despite its numerous benefits, CNC machining presents certain challenges. These limitations arise mainly from initial costs, complexity, and specific material constraints.
High Initial Investment
The cost of CNC machines can be prohibitive for small businesses. These advanced machines require significant upfront investment, which includes both the equipment and setup.
Complexity of Operation
Operating CNC machinery demands skilled labor. Operators must understand programming, machine maintenance, and troubleshooting to ensure seamless production.
Material Limitations
While CNC can handle many materials, not all are suitable. Some materials, especially exotic alloys or brittle substances, may pose challenges in machining processes.
Key Challenges of CNC Machining
- Cost-Intensive: High initial purchase and maintenance costs.
- Skill Requirements: Need for trained professionals.
- Material Restrictions: Not all materials are easily machined.

Understanding these challenges is crucial for effective implementation. Proper planning and investment in training can help mitigate these limitations, optimizing the advantages CNC technology offers.
CNC in Modern Manufacturing: Industry Applications
CNC technology plays a pivotal role in transforming modern manufacturing. Its precision, efficiency, and versatility make it indispensable across various industries.
Aerospace and Automotive Industries
In aerospace, CNC machining is crucial for producing complex components with tight tolerances. The automotive industry also relies on CNC for large-scale production of custom metal parts and engine components.
Electronics and Medical Sectors
CNC machines manufacture precision electronics, ensuring each tiny part meets stringent specifications. Similarly, the medical sector utilizes CNC machining for creating complex devices and implants, thanks to its ability to produce intricate details accurately.
General Manufacturing Applications
CNC's influence extends to general manufacturing, where it's used to craft everyday products with high precision. This includes consumer goods and industrial equipment parts.
Key Industry Applications of CNC Technology
- Aerospace: Complex, precise components.
- Automotive: Mass production and custom parts.
- Electronics and Medical: High-detail, precision items.

Embracing CNC technology allows industries to innovate, improve production quality, and maintain competitiveness in a rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape.
The Future of CNC: Trends and Innovations
CNC technology is constantly evolving, integrating with cutting-edge advancements to enhance manufacturing processes. One major trend is the integration of CNC with the Internet of Things (IoT), allowing machines to communicate for optimized production.
Advanced Automation and Smart Manufacturing
CNC systems are increasingly adopting automation, enabling them to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. The rise of smart manufacturing integrates advanced sensors to monitor performance and ensure high precision and efficiency.
Emerging Trends in CNC Technology
- IoT Integration: Connectivity for intelligent manufacturing.
- Advanced Automation: Increased efficiency with less manual input.
- Smart Sensors: Enhanced quality control and process optimization.

These innovations position CNC technology at the forefront of Industry 4.0. As CNC machines continue to advance, they empower manufacturers to achieve greater precision, speed, and scalability in production. This progress heralds a new era of possibilities in manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions About CNC
Many people have questions about CNC and its uses. Here, we address some common inquiries.
What is the main use of CNC?
CNC is primarily used in manufacturing for precision machining. It automates complex processes to produce accurate and consistent parts.
Are there different types of CNC machines?
Yes, there are various types, including mills, lathes, and routers. Each serves specific functions in manufacturing.
How do you learn CNC programming?
Learning CNC programming can involve taking classes, online courses, or apprenticeship programs. Many resources are available for different learning styles.
What industries use CNC machines?
CNC machines are prevalent in aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics industries. Their versatility makes them valuable in many sectors.
Can CNC machines work with any material?
CNC machines can work with a wide range of materials, such as metals, plastics, and wood. Material choice depends on the application.
Additional FAQs:
- What does CNC stand for?
- Is CNC machining eco-friendly?
- How does CNC improve product quality?
These FAQs help clarify the basics and uses of CNC technology for newcomers.
How to Get Started: CNC Classes, Online Resources, and Career Paths
Getting started with CNC can be both exciting and challenging. There are various avenues to begin your journey.
One of the most accessible ways is through local classes. Search for "CNC classes near me" to find options. Community colleges and vocational schools often offer comprehensive courses.
Online resources provide flexibility and convenience. Platforms like Titan CNC Academy offer detailed tutorials and lessons. These programs can fit any schedule, making them ideal for self-paced learning.
Once trained, there are numerous career paths. CNC operators, machinists, and programmers are in high demand across industries. Many companies provide on-the-job training, advancing your skills further.
Ways to Start with CNC:
- Local classes and workshops
- Online courses and certifications
- Apprenticeship programs
- On-the-job training
Each path offers unique benefits and opportunities. Investing time in learning CNC can lead to a rewarding career in a growing industry.

Conclusion: Why CNC Matters in Today’s World
CNC technology plays a pivotal role in modern manufacturing. It brings precision, efficiency, and innovation to various industries. From automotive to electronics, CNC machining is indispensable.
The ability to produce complex parts with consistency has transformed industries. CNC machining supports mass production and rapid prototyping, making it vital for product development.
As industries evolve, CNC continues to adapt. Its integration with digital technologies and automation highlights its significance. Understanding and leveraging CNC can unlock endless possibilities in manufacturing advancements.